Aquí os dejo unos breves apuntes sobre Read-Only Domain Controllers en Windows 2008, un video de como instalarlo y enlaces oficiales de Microsoft, que incluyen:
- Whitepaper: Planning and Deploying Read-Only Domain Controllers
- TechNet: Deploying RODCs in the Perimeter Network
- TechNet: Administering RODCs in Branch Offices
Using Read-Only Domain Controllers
----------------------------------------------------
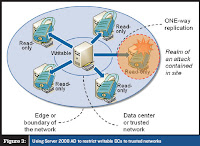
The RODC is designed to address the branch office scenario.
An RODC is a DC that maintains a copy of all objects in the domain and all Attributes except confidential attributes (secrets) such as password-related properties. When a user in the branch office logs on, the RODC receives the
request and forwards it to a DC in the hub site for authentication.
You are able to configure a password replication policy (PRP) for the RODC that specifies user accounts the RODC is allowed to cache. If the user logging on is included in the PRP,the RODC caches that user’s credentials so that the next time the user requests authentication, the RODC can perform the task locally. As users who are included in the PRP log on, the RODC builds its cache of credentials so that it can perform authentication locally for those users.
Deploying an RODC
----------------------------------
The high-level steps to install an RODC are as follows:
1. Ensure that the forest functional level is Windows Server 2003 or higher.
2. If the forest has any domain controllers running Microsoft Windows Server 2003, run
adprep /rodcprep
3. Ensure that at least one writable domain controller is running Windows Server 2008
4. Install the RODC.
If you are upgrading an existing forest to include DCs running W2008, you must run the command adprep /rodcprep.
This command configures permissions so that RODCs are able to replicate DNS application directory partitions. If you are creating a new Active Directory forest that contains only DCs running W2008, you do not need to run adprep /rodcprep.
You can find the adprep command in the cdrom\Sources\Adprep folder of the Windows Server 2008 installation DVD.
An RODC must replicate domain updates from a writable DC running W2008, and the RODC must be able to establish a replication connection with the writable W2008 DC.
Ideally, the writable W2008 DC should be in the closest site—the hub site. If you want the RODC to act as a DNS server, the writable W2008 DC must also host the DNS domain zone.
Installing an RODC
--------------------------------------
After you complete the preparatory steps, you can install an RODC on either a full or Server Core installation of W2008. On a full installation of W2008, you can use the Active Directory Domain Services Installation Wizard to create an RODC.
You select Read-Only Domain Controller (RODC) on the Additional Domain Controller Options page of the wizard
Alternatively, you can use the dcpromo command with the /unattend switch to create the RODC.
On a Server Core installation of W2008, you must use the dcpromo /unattend command.
Your answer file would be similar to the following:
[DCInstall]
Username=Pepe_Perez
Password=P@ssw0rd
UserDomain=windowsmeconfunde.internal
InstallDns=yes
ConfirmGC=yes
ReplicaOrNewDomain=ReadOnlyReplica
ReplicaDomainDNSName=windowsmeconfunde.internal
Sitename=MyBranch
databasePath="e:\ntds"
logPath="e:\ntdslogs"
sysvolpath:"f:\sysvol"
SafeModeAdminPassword:P@ssw0rd
RebootOnCompletion:yes
Password Replication Policy
----------------------------------------
PRP determines which users’ credentials can be cached on a specific RODC. If PRP allows an RODC to cache a user’s credentials, that user’s authentication and service ticket activities can be processed by the RODC. If a user’s credentials cannot be cached on an RODC, authentication and service ticket activities are referred to a writable domain controller by the RODC.
An RODC PRP is determined by two multivalued attributes of the RODC computer account.
These attributes are known as:
- Allowed List
-----------------
If a user’s account is on the Allowed List, the user’s credentials are cached. You can include groups on the Allowed List, in which case, all users who belong to the group can have their credentials cached on the RODC.
- Denied List
------------
If a user’s account is on the Denied List, the user’s credentials are not cached. You can include groups on the Denied List, in which case, all users who belong to the group can not have their credentials cached on the RODC.
If a user is on both the Allowed List and the Denied List, that user’s credentials will not be cached—the Denied List takes precedence
Configuring Domain-Wide Password Replication Policy
-----------------------------------------------------------
To facilitate the management of PRP, W2008 creates two domain local security groups in the Users container of AD DS.
- Allowed RODC Password Replication Group
-------------------------------------------
Is added to the Allowed List of each new RODC. By default, the group has no members.
Therefore, by default, a new RODC will not cache any user’s credentials. If there are users whose credentials you want all domain RODCs to cache, add those users to the Allowed RODC Password Replication Group.
- Denied RODC Password Replication Group
------------------------------------------
It is added to the Denied List of each new RODC. If there are users whose credentials you want to ensure domain RODCs never cache, add those users to the Denied RODC Password Replication Group. By default, this group contains security-sensitive accounts that are members of groups such as Domain Admins, Enterprise Admins, and Group Policy Creator Owners.
Configuring an RODC-Specific Password Replication Policy
---------------------------------------------------------------
The Allowed RODC Password Replication Group and Denied RODC Password Replication
Group provide a method of managing PRP on all RODCs. However, you typically need to
allow the RODC in each branch office to cache user and computer credentials for that specific location. Therefore, you must configure the Allowed List and the Denied List of each RODC.
To configure an RODC PRP, open the properties of the RODC computer account in the
Domain Controllers OU. On the Password Replication Policy tab, you can view the current PRP settings and add or remove users or groups from the PRP.
Administering Credentials Caching on an RODC
-----------------------------------------------------
When you click the Advanced button on the Password Replication Policy tab,the Advanced Password Replication Policy dialog box appears.
The drop-down list at the top of the Policy Usage tab enables you to select one of the following RODC reports:
- Accounts Whose Passwords Are Stored On This Read-Only Domain Controller--------------------------------------------------------------------------
This report displays the list of user and computer credentials currently cached on the RODC. You can use this list to determine whether credentials are being cached that you do not want to be cached on the RODC and modify the PRP accordingly.
- Accounts That Have Been Authenticated To This Read-Only Domain Controller
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
This report displays the list of user and computer credentials that have been referred to a writable domain controller for authentication or service ticket processing. You can use this list to identify users or computers that are attempting to authenticate with the RODC. If any of these accounts are not being cached and you want them to be, add them to the PRP.
The Resultant Policy tab of the Advanced Password Replication Policy dialog box enables
you to evaluate the effective caching policy for an individual user or computer.
Click Add to select a user or computer account for evaluation.
Video: How install a RODC
--------------------------------------------
More Inf:
-----------------
Planning and Deploying Read-Only Domain Controllers
A read-only domain controller (RODC) is a new type of domain controller in the Windows Server® 2008 operating system. This guide explains what RODCs are and how they function. See the Overview below for links to other guides about how to deploy them in various scenarios.
http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=AE33A129-FF41-4BEC-B2B7-6DDCD4998828&displaylang=en
Deploying RODCs in the Perimeter Network
This topic describes how to deploy a read only domain controller (RODC) in a perimeter network, thereby extending the corporate forest into the perimeter network.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd728035(WS.10).aspx
Administering RODCs in Branch Offices
This topic provides guidelines for common administrative tasks for read-only domain controllers (RODCs) in branch offices:
-Using Remote Desktop to administer RODCs in branch offices
-Reestablishing replication for an RODC
-Checking the lastLogonTimeStamp attribute on an RODC to discover stale accounts in a branch office
-Resolving an account lockout problem in a branch office with an RODC
-Performing backups of an RODC
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd736126(WS.10).aspx
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario